Environment arguments
Developer's Note:
The EnvironmentArgument is deprecated and will be removed in a future version!
If you still want some form of an "environment variable", you can implement it using a MultiLiteralArgument or a CustomArgument with the three values: normal, nether, end!
For reference, the old documentation is outlined below:
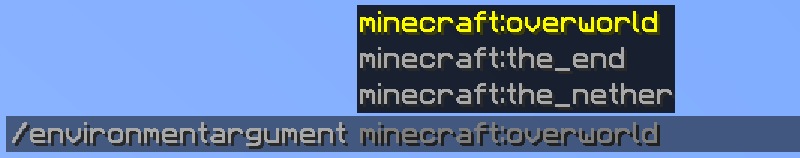
The EnvironmentArgument class allows a command sender to refer to a specific world environment, declared in Bukkit's World.Environment class. This includes the following three environments: NORMAL, NETHER and THE_END.
Example - Creating a new world
Say we want to create a new world on our Minecraft server. To do this, we need to know the name of the world, and the type (i.e. overworld, nether or the end). As such, we want to create a command with the following syntax:
/createworld <worldname> <type>
Using the world name and the environment of the world, we can use Bukkit's WorldCreator to create a new world that matches our provided specifications:
new CommandAPICommand("createworld")
.withArguments(new StringArgument("worldname"))
.withArguments(new EnvironmentArgument("type"))
.executes((sender, args) -> {
String worldName = (String) args[0];
Environment environment = (Environment) args[1];
// Create a new world with the specific world name and environment
Bukkit.getServer().createWorld(new WorldCreator(worldName).environment(environment));
sender.sendMessage("World created!");
})
.register();
CommandAPICommand("createworld")
.withArguments(StringArgument("worldname"))
.withArguments(EnvironmentArgument("type"))
.executes(CommandExecutor { sender, args ->
val worldName = args[0] as String
val environment = args[1] as Environment
// Create a new world with the specific world name and environment
Bukkit.getServer().createWorld(WorldCreator(worldName).environment(environment))
sender.sendMessage("World created!")
})
.register()